In the digital age,pemacu kilat USB is like the“data pocket”of modern people,but the complexity of its interface form factor is often overlooked-have you ever been at a loss when transferring files in an emergency due to mismatched interfaces?From the retro USB-A to the all-around Type-C,from the anti-lost design of the“wrist version”to the chip packaging of the UDP process,behind the different interfaces are hidden performance,scenarios,and even the code of the commercial game.This article will take you to see the classification logic and evolution of the truth of the USB flash drive interface.
1、According to the physical interface type classification
(1)USB-A interface
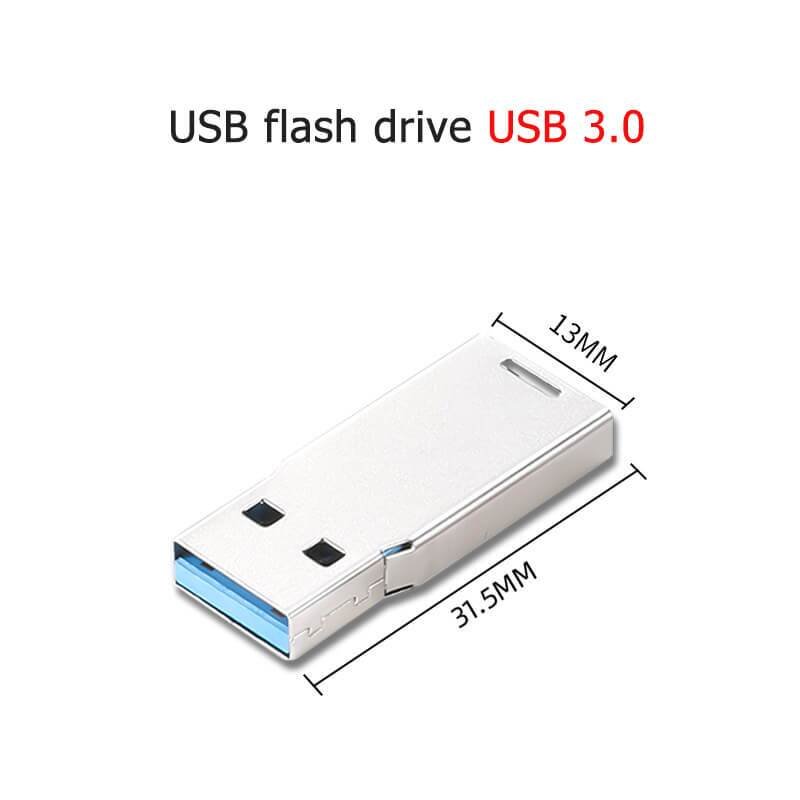
USB-A interface is our common USB flash drive USB interface,is the earliest popularity of the interface,USB-A rectangular design,compatibility,widely available in computer hosts,car equipment and other scenes.Its metal contacts are arranged in parallel,support USB 2.0 to USB 3.2 Gen1 protocol,the theoretical rate of up to 5Gbps47.The disadvantage is that the volume is large and does not support forward and reverse blind plug,gradually replaced by the new standard.
Typical applications:
Traditional desktop computers,notebook computers external storage,car multimedia system expansion.




(2)USB-C interface(Type-C)
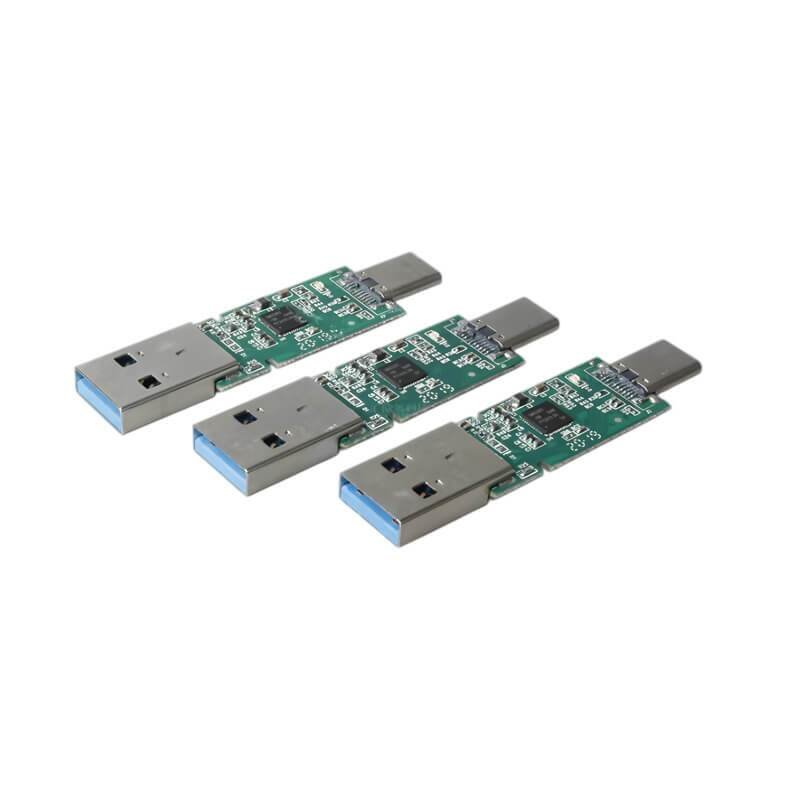
USB-C is the current mainstream interface,also we say Type-c interface,it adopts a symmetrical 24-pin design,support for forward and reverse random plug and a variety of protocols integrated(such as USB4,Thunderbolt 3/4,DP video output).The physical strength is enhanced by the reinforced contact design,and the theoretical transmission rate is up to 40Gbps(USB4 standard).
Advantage:
Multi-protocol compatible:support PD fast charging,high-speed data transmission(USB4),video output 3-in-1 function
Miniaturized design:size is only 8.4 x 2.6mm,suitable for thin and light devices
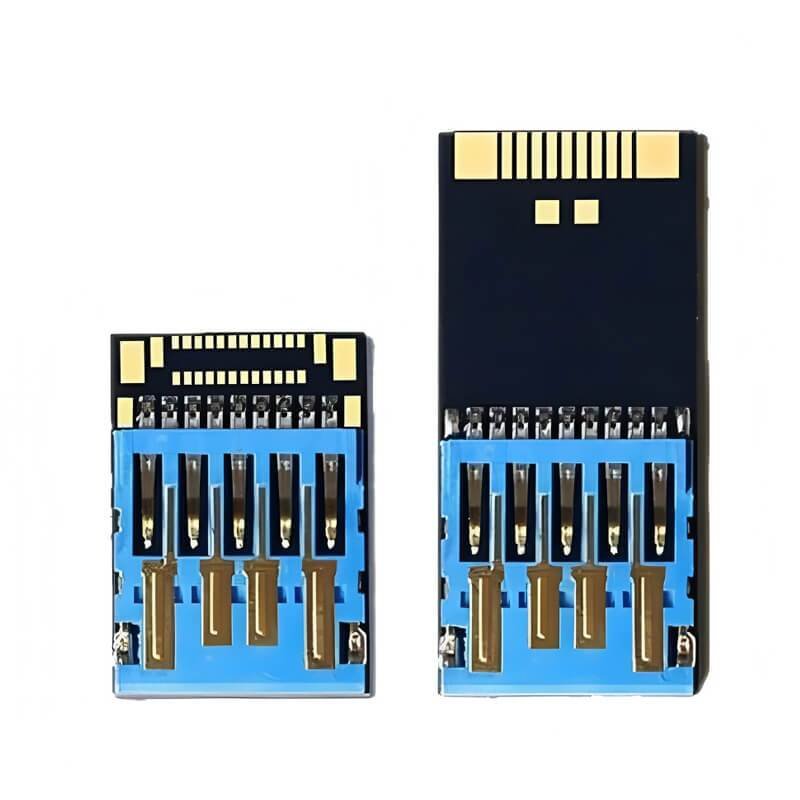
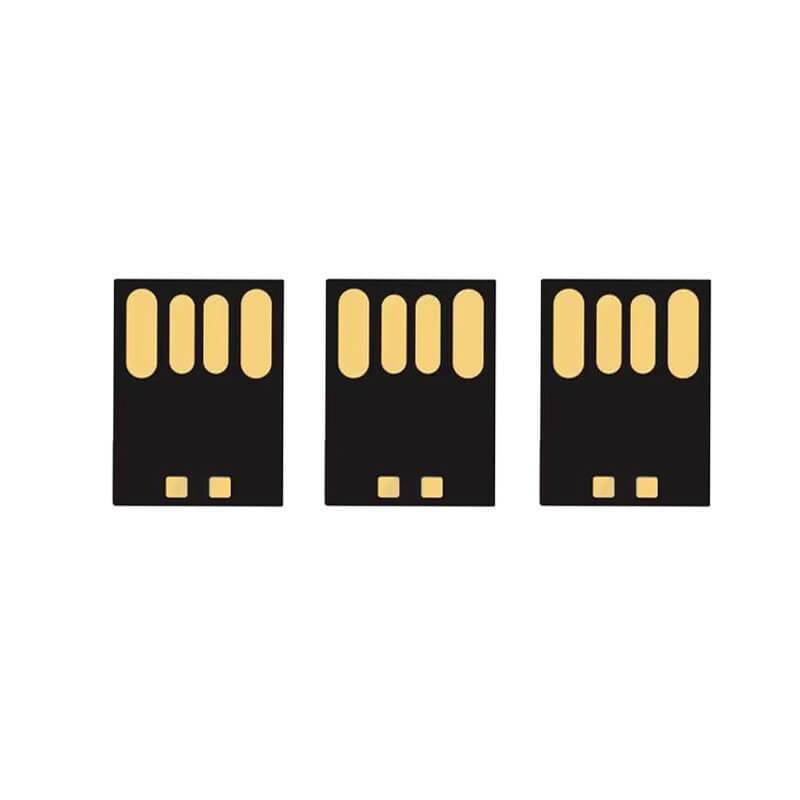
(3)UDP Interface
UDP is not a separate interface type,but a chip encapsulation technology:the main control chip and flash memory particles are encapsulated into a single unit through black epoxy resin,eliminating the need for a traditional PCB board.This technology minimizes the size of the USB flash drive(commonly found in products the size of a fingernail cover),but the heat dissipation performance is weak,and long-term high-intensity use can easily lead to aging,and our common card-type USB flash drives are all black gum chips.
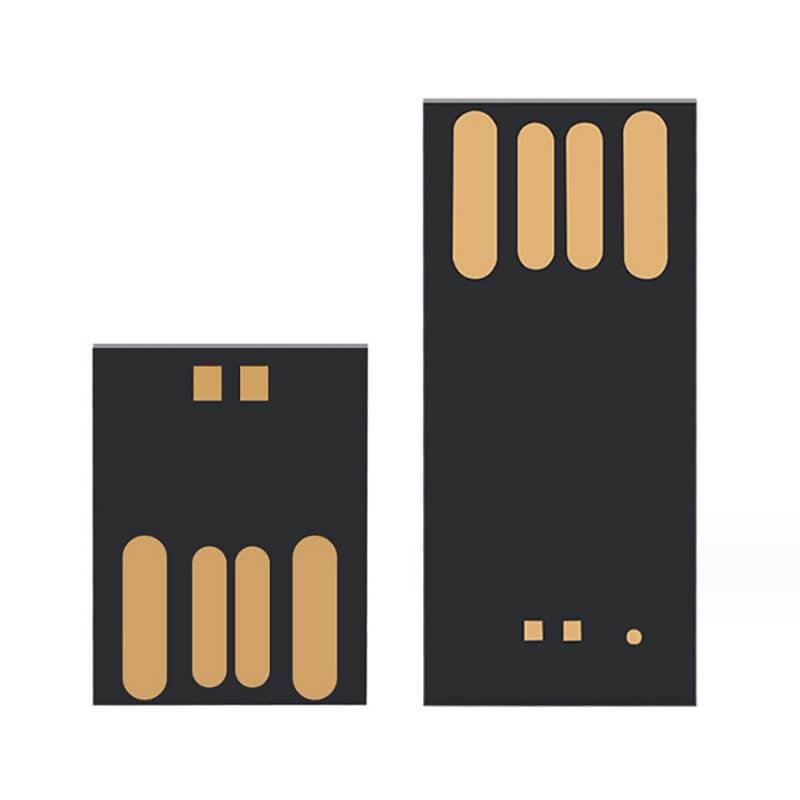
COB (chip-on-board), as know as UDP, is an integrated USB memory chip with waterproof, dustproof and high shock-resistant performance. The flash chip is manufactured using a special COB packaging process – Product in Package (PIP) technology, that makes the COB more compact and air-tight, and is safe from water damage or dust interference. It is available in both USB 2.0 & USB 3.0, and in the both standard (24.8 * 11.3 * 1.4 mm) and micro (15 * 11.3 * 1.4 mm) size.
USB Interface: USB 2.0
Memory Capacity: 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, 32GB , 64GB, 128GB
Dimension: 24.8 * 11.3 * 1.4 mm(Standard) 15 * 11.3 * 1.4 mm(Micro)
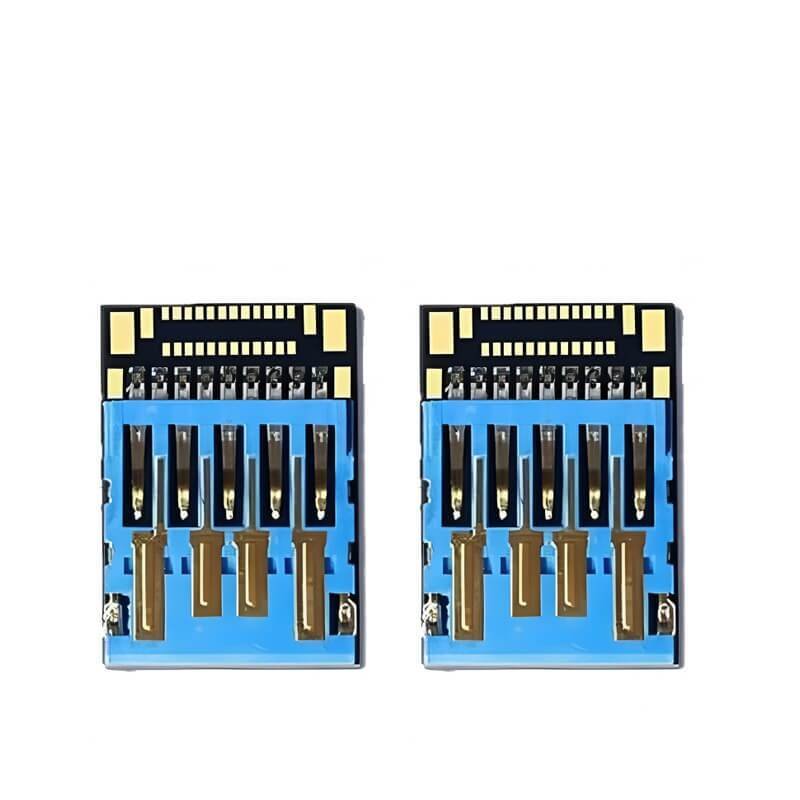


USB Interface: USB 3.0
Memory Capacity: 8GB, 16GB, 32GB , 64GB, 128GB, 256GB
Dimension: 24.8 * 11.3 * 1.4 mm((Standard) 15 * 11.3 * 1.4 mm(Micro)
(4)Micro USB interface
Once a trapezoidal micro interface for Android devices,it adopts a 5-pin design and supports USB 2.0 protocol(480Mbps)at the highest.Its physical structure is fragile,plug life of about 10,000 times,has now been fully replaced by Type-C.
Existing applications:data migration of old Android phones,low-end electronic devices to expand storage
(5)Lightning interface

Apple’s exclusive 8-pin interface,the volume of only 6.7×1.5mm,support for forward and reverse insertion but limited transmission rate(USB 2.0 level).Poor compatibility due to ecological closure,only applicable to iOS devices such as iPhone,iPad,etc.2.
Technical limitations:
Maximum transmission rate of 480Mbps,no open license,third-party accessories require MFi certification
2、According to the transmission protocol and speed classification details
(1)USB 2.0
Theoretical rate:480Mbps(actual transmission speed of about 30-40MB/s)
Technical features:
Half-duplex transmission mode,4-pin contact design(only VCC,GND,D+,D-)
Interface color is usually black or white(no uniform specification)
Applicable Scenarios:Low power consumption peripherals(mouse,keyboard),small file transfer(documents,pictures)



(2)USB 3.2 Gen1(formerly USB 3.0)
Theoretical rate:5Gbps(actual speed of about 400-500MB/s)
New 5 sets of high-speed contacts(total of 9 pins),full-duplex transmission
Interface color standardized to blue(Type-A version)
Application Scenarios:Mobile hard disk,solid-state USB flash drive,high-transfer USB flash drive,4K video clip storage



(3)USB 3.2 Gen2 (formerly USB 3.1)
Theoretical rate:10Gbps(actual speed of about 900MB-1GB/s)
Core technology:
128b/132b encoding technology,transmission efficiency increased to 97%,support for Type-C interface and Thunderbolt protocol compatibility
Typical Device:High-end mobile solid state drive(PSSD),professional-grade film and television storage media
(4)USB 3.2 Gen2×2 (former USB 3.2)
Theoretical rate:20Gbps(actual speed of about 2GB/s)
Technical Requirements:Compulsory use of Type-C interface,dual-channel transmission is required,the host controller chip needs to support PCIe NVMe.
3、Future trends
USB flash drive interface technology is moving in the direction of faster,more versatile and smarter,the future trend:the full unification of the USB-C interface,Apple,Microsoft and other manufacturers have fully shifted to USB-C,the European Union mandatory requirements for the unification of the interface of electronic products.One cable is compatible with charging,data transfer,external display,supports USB4/Thunderbolt 3 protocol,and has a very high speed limit.
From the bulky USB-A to the all-round USB-C,from the turtle speed of USB 2.0 to the extreme speed of USB4,the evolution of the USB flash drive interface has always been centered around the goal of“faster,more stable,more universal”.For ordinary users,the choice of USB-C interface+USB4 protocol USB flash drive is a solid solution for the next 3-5 years;for industrial or special scenarios,vinyl or wireless USB flash drive can take into account the durability and convenience.The progress of technology not only improves the performance,but also redefines the way people interact with the device-perhaps in the near future,the USB flash drive will completely say goodbye to the physical interface,and become a real“invisible”storage tool.



